Age Formula in Excel: Best Methods for Quick Age Calculation
Age calculation in Excel is a common requirement for HR professionals managing employee records, researchers analysing data, or anyone working with personal datasets. Although Excel doesn’t have a built-in AGE function, you can use simple formulas to calculate age accurately and efficiently. In this blog, we will show you the quickest and easiest way, using various methods, from basic calculations to more detailed formulas that provide exact years, months, and days.
If you’re new to Excel, our Introduction to Excel course will help you master essential skills like navigating the interface, understanding data types, and using basic functions. For those looking to improve their analytical skills, our Data Analysis in Excel course dives into Pivot Tables, advanced logical functions, and data insights — helping you get the most out of your Excel work.
Basic Age Calculation Formula in Excel
The easiest and most accurate way to calculate age in Excel is by subtraction the birth date from the current date and dividing the result by 365 days.
= (TODAY()-A2)/365For example, if the birth date is in cell B2, you can use the formula:
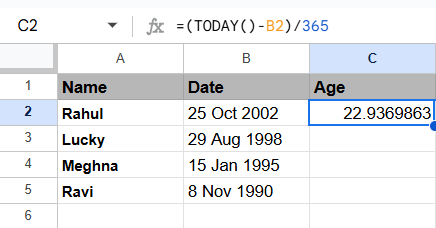
Using this formula, you can calculate your age in years, including partial years, by using a decimal. It’s simple and quick, but it’s not 100% accurate. A division by 365 ignores leap years, which can cause small errors over time. As well, it doesn’t take into account varying month lengths, which can lead to inaccurate results.
For instance, if someone was born on January 5, 2000, this formula might show 25.7 years instead of the exact 25 years and 7 months.
Accurate Methods in Excel for Age Calculation
Using INT() with YEARFRAC()
=INT(YEARFRAC(A2, TODAY(), 1))
Here’s what each part does:
YEARFRAC(start_date, end_date, basis): Calculates the fraction of years between two dates.
Basis=1: Uses the actual number of days in each month and year, ensuring accurate results, including leap years.
TODAY(): Returns the current date.
INT(): Remove the decimal part, leaving only full years.
YEARFRAC ignores leap years without the basis parameter (U.S. 30/360 method), which assumes each month has 30 days. Ages are calculated based on 1.
For example, if someone was born on March 15, 1995, this formula will return the correct age in completed years, making it reliable for most scenarios.
Using DATEDIF() for Exact Age
The DATEDIF() function (short for Date Difference) is specifically designed to calculate intervals between dates. To calculate age in completed years, use:
=DATEDIF(A2, TODAY(), "Y")The “Y” parameter ensures Excel counts only full years.
This formula provides a clean, precise integer, best used for HR records, official documents, or any scenario where exact age is required.
Why DATEDIF() is useful: Unlike simple subtraction methods, DATEDIF() counts a year only once it’s fully completed, ensuring precise results every time.
How to Calculate Age on Any Date in Excel?
1. Calculating Age on a Specific Date
Sometimes you need to calculate someone’s age by a date other than today — for example, a future hiring date, an insurance eligibility check, or a historical event. Replace the TODAY() function with the date you want to use in your formula.
Example:
=DATEDIF(A2, DATE(2026,1,31), "Y")
This formula calculates how old a person will be on January 31, 2026.
2. Getting a Detailed Age Breakdown (Years, Months, Days)
If you need a more detailed result, including years, months, and days, you can extend the formula like this:
=DATEDIF(A2, DATE(2024,12,31), "Y") & " years, " &
DATEDIF(A2, DATE(2024,12,31), "YM") & " months, " &
DATEDIF(A2, DATE(2024,12,31), "MD") & " days"
This formula tells you the exact age on the chosen date, broken down into full years, remaining months, and extra days.
Calculating Age in a Specific Year
In cases where only a year is given, and you need to calculate the age in that year, you can use the DATE() function:
=DATEDIF(A2,DATE(2028,12,31),"Y")
For mid-year calculations, you can adjust the month and day as needed. Example:
=DATEDIF(A2, DATE(2028, 6, 30), "Y")
This will return the age as of June 30, 2028.
Calculate Retirement or Eligibility Dates Using Excel
When someone reaches a certain age or turns a certain age (like retirement eligibility),
=DATE(YEAR(A2)+65,MONTH(A2),DAY(A2))
This formula calculates when someone will turn 65 based on their birth date plus 65 years.As a result, an Excel date value shows exactly when they will reach a milestone.
For more complex scenarios where you need to find out when someone reaches a certain age for months:
=DATE(YEAR(A2)+30,MONTH(A2)+6,DAY(A2))
This Excel formula finds when someone will be 30 years and 6 months old, which is useful for meeting eligibility requirements with both year and month specifications.”
Age Calculator
Points to Remember When Calculating Age in Excel
To ensure your age calculations in Excel are both accurate and reliable, keep these tips in your mind:
Use DATEDIF() or YEARFRAC() for the best accuracy. DATEDIF() is designed specifically for calculating date differences, while YEARFRAC with basis=1 considers actual calendar days, including leap years.
Apply INT() or ROUNDDOWN() to remove decimals if you only want completed years instead of fractional results.
The basic =(TODAY()-A2)/365 formula ignores leap years and varying month lengths, which can cause small inaccuracies over time.
Always confirm that your data is stored as valid Excel dates, not text. Incorrect formatting is a common cause of formula errors.
For large datasets, consider storing formulas as named ranges or on a separate calculation sheet to make your workbook easier to manage and update.
Verify your formulas by testing with special cases, such as birthdays on February 29 (leap years) or dates near the end of a month, to ensure your calculations remain accurate.
Conclusion
The fastest and easiest way to calculate age in Excel is with the DATEDIF() function. Calculate your age in years or even get a detailed breakdown by year, month, or day with just one formula.
Note:- The DATEDIF function is hidden in Excel, so type its full name and begin entering references.
So, the next time you’re working with DOB data, let Excel do the hard work for you!
FAQs
What is the formula to calculate age in Ms Excel?
=DATEDIF(A2, TODAY(), "Y")
Which Excel function is best for age calculation \?
How to calculate age in months only?
How to calculate age in days in Excel?
=TODAY()-A2
This returns the exact number of days since birth.
How to calculate retirement age in Excel?
=DATE(YEAR(A2)+60, MONTH(A2), DAY(A2))
This shows the exact date of retirement.